* thruk.conf # shipped default Thruk config
* cgi.cfg # the cgi.cfg is read on every request
* thruk_local.d/*.{cfg,conf} # local override drop dir
* thruk_local.conf # local override of Thruks settings
Config Files
Base configuration is managed in these configuration files (in the order in which they are read):
| All configuration options described in this file should go into the thruk_local.conf or into separate files below thruk_local.d/ |
Config file merge order
Single key/value settings are overridden in the order above. Nested key/value pairs like Backends are merged.
ex.:
thruk.conf: default_theme = Thruk
thruk_local.conf: default_theme = Company
results in default_theme = Company
nested values:
thruk.conf: <initial_menu_state> General = 1 Current_Status = 1 </initial_menu_state>
thruk_local.conf: <initial_menu_state> Current_Status = 0 Bookmarks = 1 </initial_menu_state>
results in
<initial_menu_state> General = 1 Current_Status = 0 Bookmarks = 1 </initial_menu_state>
List values are concatenated.
ex.:
command_enabled = 1-4 command_enabled = 33, 34
results in:
command_enabled = 1-4, 33, 34
However, if you want to override a list value completely, you can reset the list by setting it to an empty value:
command_enabled = 1-4 command_enabled = command_enabled = 33, 34
results in:
command_enabled = 33, 34
thruk.conf
The thruk.conf contains the shipped defaults. You should not edit this file directly. Overwrite your settings in your thruk_local.conf / thruk_local.d/ instead.
thruk_local.d
new in release v2.00Local settings drop directory. All *.cfg and \*.conf files in here override settings from the
thruk.conf file. Besides the standard file extension cfg and conf it is
also possible to use the hostname. Those files are only used if the hostname
matches the actual system hostname. This is a good way to separate test and
production configuration.
example:
/etc
`-- thruk
`-- thruk_local.d
|-- my.cfg # will be read on every host
`-- test.test-machine # will only be read on a host named `test-machine`
thruk_local.conf
The thruk_local.conf should contain all settings which are locally overridden. Keep the default settings in the thruk.conf and only put local overrides in either the thruk_local.conf or into conf file below thruk_local.d/.
Other config files
* cgi.cfg # Naemon/Nagios cgi.cfg * log4perl.conf # Logging configuration * menu.conf # Thruks default side navigation * menu_local.conf # local override for the navigation
cgi config
menu config
log4perl config
General Settings
title_prefix
set the title prefix for all urls this piece of text will be prepended to all page titles.
ex.:
title_prefix = Prod
use_bookmark_titles
Sets the page title to the name of a bookmark if the url matches. Private bookmarks are processed first and the name of the first match is used.
ex.:
use_bookmark_titles = 1
use_dynamic_titles
Uses more descriptive page titles. Bookmark titles take precedence and can be overridden by adding the title parameter on most pages
ex.:
use_dynamic_titles = 1
url_prefix
Changes the usual url path for Thruk. Don’t change it unless you plan to run multiple Thruk instances on the same webserver. You will have to change your fastcgi configuration too.
ex.:
url_prefix = /
use_timezone
DEPRECATED use server_timezone now.
server_timezone
new in release v2.22Changes the timezone from the systems default to this timezone.
Only set this if you have trouble with displaying the right timestamps.
Use /usr/share/zoneinfo on most linux systems for reference, as some
timezones are set using the Region/Country format.
ex.:
server_timezone = CET
default_user_timezone
new in release v2.22Since users can change their timezone setting, this changes their default. Possible values are:
-
"Server Setting"
-
"Local Browser"
-
all from
/usr/share/zoneinfo
ex.:
default_user_timezone = "Server Setting"
cluster_enabled
new in release v2.24Set to 1 to enable cluster features or 0 for single node setups.
ex.:
cluster_enabled = 1
cluster_nodes
new in release v2.24Define generic url pattern to connect all cluster nodes. Each
cluster node must be available on the given address.
3 variables will be replaced to make this url generic:
- $hostname$: hostname from hostname
- $url_prefix$: contains the url prefix from url_prefix
- $proto$: trying to autodetect either http or https, autodetect
will only work with OMD and falls back to http otherwise.
ex.:
cluster_nodes = https://$hostname$/$url_prefix$/
cluster_node_stale_timeout
new in release v2.24Set timeout after which a node is removed from the cluster.
ex.:
cluster_node_stale_timeout = 120
rest_api_enabled
DEPRECATED: setting this has no effect with Thruk 2.34 or later.
The rest api is enabled by default, disabling it would break Thruk operation.
api_keys_enabled
new in release v2.24Using api keys can be disabled by setting this to 0. You cannot use api keys at all if this is disabled.
Note: this value cannot be overridden on a per user/group basis because it is
used on pre-authentication stage. If you want users to not create new keys, use
max_api_keys_per_user = 0.
ex.:
api_keys_enabled = 1
max_api_keys_per_user
new in release v2.32Limit amount of keys a user may create. Set to 0 to disable creating new keys completely
ex.:
max_api_keys_per_user = 10
mobile_agent
DEPRECATED: setting this has no effect with Thruk 3.x or later. Specify user agents which will be redirected to the mobile plugin (if enabled).
ex.:
mobile_agent=iPhone,Android,IEMobile
default_theme
Default theme to use for all users. Must be a valid sub directory in
the themes_path folder.
ex.:
default_theme = Light
default_theme_dark
Default theme to use for if the user prefers a dark theme.
ex.:
default_theme_dark = Dark
first_day_of_week
Set first day of week. Used in reports. Sunday: 0 Monday: 1
ex.:
first_day_of_week = 1
report_use_temp_files
Large reports will use temp files to avoid extreme memory usage. With 'report_use_temp_files' you may set the report duration in days which will trigger the use of temp files. Default is 14days, so for example the 'last31days' report will use temp files, the 'thisweek' not. Can be disabled by setting to 0.
ex.:
report_use_temp_files = 14
report_max_objects
Don’t create reports with more hosts / services than this number. The purpose is to don’t wrack the server due to extended memory usage. Increase this number if you hit that limit and have plenty of memory left.
ex.:
report_max_objects = 1000
report_include_class2
Include messages with class = 2 (program messages) in reports. Setting this to 0 allows the MySQL backend to use indexes efficiently
-
0 = off
-
1 = auto (default)
-
2 = on
ex.:
report_include_class2 = 1
report_update_logcache
Should thruk update the logcache databases before running reports? Setting this to 0 reduces the time taken to run reports but the most recent data is not necessarily available. If you use this option you should probably create a cron to run "thruk -a logcacheupdate"
ex.:
report_update_logcache = 1
start_page
This link is used as startpage and points usually to the main.html with displays version information and general links.
ex.:
start_page = /thruk/main.html
home_link
This link is used whenever you click on one of the main logos. By default those logos are the Thruk logos and the link will take you to the Thruk homepage. Replace this with where you want your home location to be.
ex.:
home_link = https://www.thruk.org
home_link_target
This sets how the home link is opened. By default this is set up open in a new tab (_blank).
ex.:
home_link_target = _blank
documentation_link
This link is used in the side navigation menu as link to the documentation. Replace with your documentation location. Set it to a blank value if you don’t want a documentation link in the menu at all.
ex.:
documentation_link = /thruk/docs/
all_problems_link
Customizable link for the 'problems' link in side menu. Can be useful to reflect your companies process of error handling.
ex.:
all_problems_link = /thruk/cgi-bin/status.cgi?...
allowed_frame_links
List of allowed patterns, where links inside frames can be set to. You can link to /thruk/frame.html?link=http://wiki.my-company.com/page/blah Your wiki will then be displayed with the Thruk navigation frame. Useful for other addons, so they don’t have to display a own navigation. Wildcards are allowed since v3.06.
ex.:
allowed_frame_links = http://intranet.my-company.com allowed_frame_links = https://wiki.my-company.com allowed_frame_links = *.my-company.com # allow all links from my-company.com allowed_frame_links = https://* # allow all https links from anywhere allowed_frame_links = * # allow everything (not recommended)
link_target
List of (target, regex) pairs. When Thruk generates links (for example for the
action_url of a service) the URL is matched against the regex. If the regex
matches the URL then the 'target' is used for the links target attribute. Target
'main' is special, if the link matches allowed_frame_links, it creates a link
that is, when clicked on, opened inside a frame in Thruk. If it doesn’t match
allowed_frame_links the target '_blank' is used.
ex.:
allowed_frame_links = example.com link_target = _blank ^https?://cannot-run-in-frame.example.com/bar link_target = main ^https?://wiki.example.com/foo
max_process_memory
Maximum memory usage (in MB) at which a Thruk process will exit after finishing its request. Only affects the fcgid daemon.
ex.:
max_process_memory=1000
cli_graph_timeout
Timeout after which thruk -a graph fails. Defaults to 30.
Authorization Settings
can_submit_commands
Set this if a contact should be allowed to send commands unless defined for the contact itself. This is the default value for all contacts unless the user has a can_submit_commands setting in your monitoring configuration.
ex.:
can_submit_commands = 1
command_disabled
Use this to disabled specific commands. Can be use multiple times to disabled
multiple commands. The number can be found in the 'cmd_typ' cgi parameter from
links to the command page.
If you only want to allow a few commands, use command_enabled instead.
You may use ranges here.
If you want to disable all commands, you can use command_disabled = 0-999
or set the authorized_for_read_only role.
See a list of available commands along with their ids on the commands page.
ex.:
command_disabled = 14 command_disabled = 35 command_disabled = 17-34,50-65
command_enabled
Enable only specific commands. Overrides command_disabled setting by only
allowing a few specific commands and disabling all others. The syntax is the
same as in command_disabled. When using command_enabled then all commands
are disabled and only those from command_enabled can be used.
See a list of available commands along with their ids on the commands page.
ex.:
command_enabled = 1-4 # allow adding and removing comments command_enabled = 33,34,51,52 # allow acknowledgments command_enabled = 55,56,78,79 # allow downtimes
make_auth_user_lowercase
Convert authenticated username to lowercase.
ex.:
make_auth_user_lowercase = 1
make_auth_user_uppercase
Convert authenticated username to uppercase.
ex.:
make_auth_user_uppercase = 1
make_auth_replace_regex
Convert authenticated username by regular expression. The following example removes everything after an @ from the authenticated username and 'user@domain' becomes just 'user'.
ex.:
make_auth_replace_regex = s/^(.*?)@.*/$1/gmx
use_strict_host_authorization
When set to a true value, every contact will only see the hosts where he is contact for plus the services where he is contact for. When disabled, a host contact will see all services for this host regardless of whether he is a service contact or not.
ex.:
use_strict_host_authorization = 1
csrf_allowed_hosts
Allow specific hosts to bypass the csrf protection which requires a generated token to submit certain post requests, for example to send commands. Use comma separated list or multiple configuration attributes. Wildcards are allowed.
ex.:
csrf_allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1 csrf_allowed_hosts=192.168.*
disable_user_password_change
Disable the possibility for a user to change his password.
Only works with htpasswd passwords. To make this work
you have to set a htpasswd entry in the
Config Tool section.
ex.:
disable_user_password_change = 1
user_password_min_length
Sets the minimum length a password must have for users changing their passwords. Admins still can change the password any way they want in the config tool. This just affects the user password reset.
ex.:
user_password_min_length = 5
basic_auth_enabled
new in release v2.36Show the basic auth user / password form. Enabled when using cookie auth. You may want to set this to 0 if you only use oauth2 authentication. Set it to 2, if you want to only show the oauth2 authentication but also have a toggle button, which can display the basic auth login form as a fallback.
ex.:
basic_auth_enabled = 1
Path Settings
log4perl_conf
The path to your log4perl configuration file.
ex.:
log4perl_conf = ./log4perl.conf
thruk_verbose
verbosity / debug level same as setting THRUK_VERBOSE environment.
-
0= info / warnings (default) -
1= verbose -
2= debug -
3= enables performance debug output for each request (same as THRUK_PERFORMANCE_DEBUG=3 in env) -
4= trace
ex.:
thruk_verbose = 0
thruk_author
Enable author tweaks. Same as setting THRUK_AUTHOR environment. Only required for development, disables caches, enables template strict mode and more.
ex.:
thruk_author = 1
slow_page_log_threshold
If a page takes longer to render than this amount of seconds, a profile will be logged. Set to 0 to disable logging completely.
ex.:
slow_page_log_threshold = 30
machine_debug_info
Set level of machine information send in bug reports.
Possible options:
- prod contains release information (default)
- full contains uname and release information
- none no information
ex.:
machine_debug_info = prod
audit_logs
Defines an optional separate logfile with some extra audit relevant log
entries. The different categories can be used to enable/disabled specific
messages. The logfile can use strftime format pattern to for ex.: add the
timestamp to the logfile.
ex.:
<audit_logs> logfile = /var/log/audit/thruk-%Y.%m.%d.log # if set, audit log will be appended to this file. strftime format can used in the filename. login = 1 # log if user logs in logout = 1 # log if user logs out session = 0 # session creation / cleanup external_command = 1 # log external commands configtool = 1 # log changes made with the config tool </audit_logs>
plugin_path
Path to your plugins directory. Can be used to specify different location for you Thruk plugins. Don’t forget to set appropriate apache alias or rewrite rules when changing the plugin path. Otherwise the static content from plugins is not accessible.
Example redirect rule for apache:
ex.:
plugin_path = ./plugins
plugin_registry_url
Url to Thruks plugin registry. The url must supply a json data structure with a list thruk plugins. Can be specified multiple times.
ex.:
plugin_registry_url = https://api.thruk.org/v1/plugin/list
themes_path
Path to your themes directory. Can be used to specify different location for you Thruk themes. Don’t forget to set appropriate apache alias or rewrite rules when changing the themes path. Otherwise the static content from your themes may not accessible.
ex.:
themes_path = ./themes
var_path
Path to the var directory. Thruk stores user specific date here.
ex.:
var_path = ./var
tmp_path
Path to a temporary directory. Defaults to /tmp if not set and usually this is a good place.
ex.:
tmp_path = /tmp
ssi_path
The path to your ssi (server side includes) files. See Server Side Includes for details.
ex.:
ssi_path = ssi/
user_template_path
Specify a additional directory for user supplied templates. This makes it easy to override thruks own templates. Template search order is:
-
users template path
-
themes template path
-
plugins template path
-
thruks template path
ex.:
user_template_path = ./my_templates
logo_path_prefix
Changes the path to your logo images. Default is $url_prefix+'thruk/themes/'$current_theme'/images/logos/' and therefore relative to the current selected theme. You could set a fixed path here. Like usual, paths starting with a / will be absolute from your webserver root directory. Paths starting without a / will be relative to the cgi directory.
ex.:
logo_path_prefix = /icons/
physical_logo_path
Location of your logos in your filesystem. This directory should be mapped to your 'logo_path_prefix' directory where 'logo_path_prefix' is the path relative to your webserver root directory and 'physical_logo_path' is the corresponding filesystem path.
ex.:
physical_logo_path = /usr/share/icons/
mode_file
Mode used when creating or saving files.
ex.:
mode_file = 0660
mode_dir
Mode used when creating folders
ex.:
mode_dir = 0770
resource_file
Set a general resource file. Be warned, if any macros contain sensitive data like passwords, setting this option could expose that data to unauthorized user. It is strongly recommended that this option is only used if no passwords are used in this file or in combination with the 'expand_user_macros' option which will limit which macros are exposed to the user. Instead of using a general 'resource_file' you could define one file per peer in your peer config.
ex.:
resource_file = /etc/nagios3/resource.cfg
Search Settings
maximum_search_boxes
new in release v2.24maximum number of allowed search boxes
ex.:
maximum_search_boxes = 9
search_long_plugin_output
Search long_plugin_output in default search, ex. from the side navigation. It is enabled by default, but can have significant performance impact in larger setups.
ex.:
search_long_plugin_output = 1
default_service_filter
new in release v1.86-2The default_service_filter set a default service filter which is used when no
other filter is applied (except from links to hosts or groups). The filter is
negated by a leading exclamation mark. The example filters out all services starting
with "test_". You can use regular expressions. The Default is not set.
ex.:
default_service_filter = !^test_
default_main_filter
new in release v3.06The default main filter can be use to apply a filter to the "All Hosts" view on the main landing page. You can use a special variable $REMOTE_USER$ which will be replace by the current user. The following example will apply a filter on the contact with the current user name, so the dashboard will show only hosts/service where the user is contact for, even if the user has global admin permissions.
ex.:
default_main_filter = contact = $REMOTE_USER$
main_exclude_top5_hostgroups
Exclude some hostgroups from the top 5 list on the "Home" page. The values can be regular expressions.
ex.:
main_exclude_top5_hostgroups = all_hosts, regex.*filter
Paging Settings
use_pager
DEPRECATED: setting this has no effect with Thruk 3.x or later.
Using the pager will make huge pages much faster as most people don’t want a services page with 100.000 services displayed. Can be disabled if you don’t need it.
ex.:
use_pager = 1
paging_steps
Define the selectable paging steps. Use the * to set the default selected value.
ex.:
paging_steps = *100, 500, 1000, all
group_paging_overview
Just like the paging_steps, but only for the groups overview page.
ex.:
group_paging_overview = *3, 10, 100, all
group_paging_summary
Just like the paging_steps, but only for the groups summary page.
ex.:
group_paging_summary = *10, 50, 100, all
group_paging_grid
Just like the paging_steps, but only for the groups grip page.
ex.:
group_paging_grid = *5, 10, 50, all
problems_limit
Cut off objects on problems page, set 0 to disable limit completely. Defaults to 500.
ex.:
problems_limit = 500
main_table_full
new in release v3.00Set default for showing main data table at full size or not.
ex.:
main_table_full = 0
Display Settings
host_action_icon
DEPRECATED: setting this has no effect with Thruk 3.x or later. Change path to your host action icons. You may use relative paths to specify completely different location. You also may want to use 'action_pnp.png' when using pnp. Icon can be overridden by a custom variable '_ACTION_ICON'.
ex.:
host_action_icon = action.gif
service_action_icon
DEPRECATED: setting this has no effect with Thruk 3.x or later. Change path to your service action icons. You may use relative paths to specify completely different location. You also may want to use 'action_pnp.png' when using pnp. Icon can be overridden by a custom variable '_ACTION_ICON'.
ex.:
service_action_icon = action.gif
initial_menu_state
Set initial menu state.
closed => 0 open => 1
ex.:
<initial_menu_state> General = 1 Current_Status = 1 Reports = 1 System = 1 Bookmarks = 1 </initial_menu_state>
use_frames
DEPRECATED: setting this has no effect with Thruk 3.x or later.
Set whether you want to use a framed navigation or not. With using frames it’s sometimes easier to include addons. See allowed_frame_links option for how to integrate addons.
ex.:
use_frames = 0
navframesize
DEPRECATED: setting this has no effect with Thruk 3.x or later.
Width of the navigation frame in px.
ex.:
navframesize = 190
|
To achieve a similar effect in Thruk 3.x you can create a ssi file, ex.:
|
use_new_command_box
DEPRECATED: setting this has no effect with Thruk 3.x or later.
Show the new split command box on the host / service details page.
ex.:
use_new_command_box = 1
datetime_format
Default time format. Use POSIX format.
ex.:
datetime_format = %Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S
datetime_format_long
Default long time format.
ex.:
datetime_format_long = %a %b %e %H:%M:%S %Z %Y
datetime_format_log
Default log time format.
ex.:
datetime_format_log = %B %d, %Y %H
datetime_format_trends
Default trends time format.
ex.:
datetime_format_trends = %a %b %e %H:%M:%S %Y
datetime_format_today
Default time format for todays date. Can be useful if you want a shorter date format for today.
ex.:
datetime_format_today = %H:%M:%S
info_popup_event_type
DEPRECATED: setting this has no effect with Thruk 3.x or later.
info_popup_options
DEPRECATED: setting this has no effect with Thruk 3.x or later.
show_notification_number
Display the current number of notification after the current / max attempts on the status details page.
ex.:
show_notification_number = 0
default_host_columns
new in release v2.14List of default columns on host details page. Determines which columns and the order of the displayed columns. See an example on the Dynamic Views page.
ex.:
default_host_columns = name,state,last_check,duration,plugin_output
default_service_columns
new in release v2.14List of default columns on service details page.
Determines which columns and the order of the displayed columns.
See an example on the Dynamic Views page.
Use ex.: peer_name:site to always show the site name column or optional
only if there is more than one backend with the ? as in peer_name?:site.
ex.:
default_service_columns = host_name,description,state,last_check,duration,current_attempt,plugin_output
default_overview_columns
new in release v2.38List of default columns on overview details page. Determines which columns and the order of the displayed columns. See an example on the Dynamic Views page.
ex.:
default_overview_columns = name,state,services,actions
default_grid_columns
new in release v2.38List of default columns on grid details page. Determines which columns and the order of the displayed columns. See an example on the Dynamic Views page.
ex.:
default_grid_columns = name,state,actions
show_backends_in_table
Display the backend/site name in the status table. This is useful if you have same hosts or services on different backends and need to know which one returns an error. Valid values are:
1 - show site name at the end 2 - put site name in front
ex.:
show_backends_in_table = 0
show_config_edit_buttons
Show links to config tool for each host / service. You need to have the config tool plugin enabled and you need proper permissions for the link to appear.
ex.:
show_config_edit_buttons = 1
admin_role_from_system_and_conf
new in release v3.12For historical reasons (there was no explicit admin role in the past) any user with both, the - authorized_for_system_commands and - authorized_for_configuration_information gains the full admin role as well. This behaviour can be disabled with this admin_role_from_system_and_conf switch. This is deprecated and the default will change in a future release.
show_full_commandline
Display the full command line for host / service checks . Be warned, the command line could contain passwords and other confidential data. In order to replace the user macros for commands, you have to set the 'resource_file' in your peer config or a general resource_file option.
-
0 = off, don’t show the command line at all
-
1 = show them for contacts with the role: authorized_for_configuration_information (default)
-
2 = show them for everyone
ex.:
show_full_commandline = 0
commandline_obfuscate_pattern
new in release v2.18Replace pattern for expanded command lines. Could be used to replace sensitive information from being displayed in the gui. The pattern is a simple perl regular substitute expression in the form of '/pattern/replacement/'
ex.:
commandline_obfuscate_pattern = /(\-\-password=")[^"]*(")/$1"***"$2/
commandline_obfuscate_pattern = /(check_vmware_.*\-p )(\S+)/$1"***"/
commandline_obfuscate_pattern = /(check_.*\--pw )(\S+)/$1"***"/
commandline_obfuscate_pattern = /(check_.*\"password\": )(\S+)/$1"***"/
Another way is to create a _OBFUSCATE_REGEXP custom variable which will then be used
for its host/service. The syntax is slightly different, you only set the regexp
pattern which will be replaced:
ex.:
define host {
host_name test
_OBFUSCATE_REGEXP pass\W+
}
The password can be base64 encoded to mitigate escaping issues. Encode the regexp
and add the b64: prefix.
%>echo -n "password" | base64 cGFzc3dvcmQ=
then use this in your naemon configuration:
define host {
host_name test
_OBFUSCATE_REGEXP b64:cGFzc3dvcmQ=
}
If regular expressions are not required, you can use the _OBFUSCATE_STRING custom
variable. This is a simple text replacement with no regular expressions. This also
supports the optional base64 encoding.
ex.:
define host {
host_name test
_OBFUSCATE_STRING password
}
show_full_commandline_source
Usually the source of your expanded check_command should be the check_command attribute of your host / service. But under certain circumstances you might want to use display expanded commands from a custom variable. In this case, set 'show_full_commandline_source' to '_CUST_VAR_NAME'.
ex.:
show_full_commandline_source = check_command
show_logout_button
Show additional logout button next to the top right preferences button. (works only together with cookie authentication)
ex.:
show_logout_button=1
logout_link
new in release v2.42Change url of logout link. Might be useful in combination with oauth.
ex.:
logout_link=/thruk/cgi-bin/login.cgi?logout
show_long_plugin_output
When a plugin returns more than one line of output, the output can be displayed directly in the status table, as popup or not at all. Choose between popup, inline and off
ex.:
show_long_plugin_output = popup
status_color_background
Color complete status line with status color or just the status itself.
ex.:
status_color_background=0
show_modified_attributes
Show if a host / service has modified attributes.
ex.:
show_modified_attributes = 1
show_contacts
Show host / service contacts. User must have the configuration_information role.
ex.:
show_contacts = 1
is_executing_timeout
Seconds after which the "is_executing" icons disappear.
ex.:
is_executing_timeout = 5
show_host_attempts
Show check attempts for hosts too. The default is to show them on the problems page only. Use this value to force a value.
ex.:
show_host_attempts = 1
short_link
Define pattern to be replaced with links in comments, downtimes and plugin output.
Syntax is: | regex pattern | [link name](link target) |
Can be set multiple times.
Simple links and markdown style links will be replaced automatically. So links in the form:
https://linktarget/... or [link text](https://target...)
will just work. No need to disabled escape_html just to show some links.
ex.:
short_link = |INC(\d+)|[$1](https://tickets.company.com/ticket/$1)| short_link = |GH#(\d+)|[Issue $1](https://github.com/sni/thruk/issues/$1)|
Replaces the string "INC12345" with the link:
<a href="https://tickets.company.com/ticket/12345">12345</a>
Replaces the string "GH#123" with the link:
<a href="https://github.com/sni/thruk/issues/123">123</a>
copy_paste_link
Define pattern to be replaced with copy / paste buttons in the plugin output.
Syntax is: (pre text regex pattern)(link text regex pattern)(post text regex pattern)
Can be set multiple times.
ex.:
copy_paste_link = (ticket id: ")(.*?)(")
perf_bar_mode
This option enables a performance bar inside the status/host list which create a graph from the performance data of the plugin output. Available options are 'match', 'first', 'all', 'worst' and 'off'.
match: try to set graph which matches the output all: graph all performance values available first: graph only the first performance value worst: graph only the graph for the worst state off: graph no value at all
ex.:
perf_bar_mode = match
perf_bar_pnp_popup
Show pnp popup if performance data are available and pnp is used as graph engine. The popup will be available on the performance data bar chart on the right side of each host/service. It uses the normal pnp popup logic, so you need to install the proper SSI files.
ex.:
perf_bar_pnp_popup = 1
useragentcompat
If set, a Internet Explorer (IE) compatibility header will be added to the html header.
default_state_order
Defines the order to determine the worst/best states. Used in business processes and the panorama dashboard. Can be overridden in those plugins.
ex.:
default_state_order = down, unreachable, \
unknown, critical, warning, \
acknowledged_down, acknowledged_unreachable, \
acknowledged_unknown, acknowledged_critical, acknowledged_warning, \
downtime_down, downtime_unreachable, \
downtime_unknown, downtime_critical, downtime_warning, downtime_up, downtime_ok, \
up, ok, downtime_pending, pending
shown_inline_pnp
Show inline pnp graph if available. If a service or host has a pnp4nagios action or notes url set. Thruk will show a inline graph on the extinfo page. This works for /pnp4nagios/ urls and /pnp/.
ex.:
shown_inline_pnp = 1
graph_word
graph_word is a regexp used to display any graph on the details page. if a service or host has a graph url in action url (or notes url) set it can be displayed by specifying a regular expression that always appears in this url. You can specify multiple graph_words.
|
pnp4nagios
When using pnp4nagios, no graph_word is required, just keep it empty. |
sample service configuration for graphite:
define service{
service_description Load
host_name localhost
use generic-service
action_url http://YOURGRAPHITE/render/?lineMode=connected&width=586&height=308&_salt=1355923874.899&target=cactiStyle($HOSTNAME$.$SERVICEDESC$.*)&xFormat=%25H%3A%25M&tz=Europe/Paris
check_command check_load
}
ex.:
graph_word = /render/ # for graphite
|
quotes
Quotes are supported in the action_url statement, you may want to use it for special graphite function (http://graphite.readthedocs.org/en/1.0/functions.html) Do not escape double quotes here, otherwise graph won’t work. |
graph_replace
graph_replace is another regular expression to rewrite special characters in the url. For example graphite requires all non-word characters replaced by underscores while graphios needs spaces removed too. You can use this setting multiple times.
sample service configuration for graphite:
graph_replace = s/[^\w\-]/_/gmx
sample service configuration for graphios:
graph_replace = s/\s//gmx graph_replace = s/[^\w\-]/_/gmx
http_backend_reverse_proxy
The http_backend_reverse_proxy will proxy requests for pnp or grafana action_urls via the http backend if possible. This only works for http backends and if cookie auth is enabled. Can be used to proxy thruk nodes (experimental)
Possible options:
- 0 disabled
- 1 enabled
ex.:
http_backend_reverse_proxy = 1
show_custom_vars
Show custom vars in host / service ext info. List variable names to display in the host and service extinfo details page. Can be specified more than once to define multiple variables. You may use html in your variables. Use * as wildcard, ex.: _VAR* To show a host custom variable for services, prepend _HOST, ex.: _HOSTVAR1. To show all host variables in the service view, use wildcards, ex.: _HOST* Host variables are only used with HOST*, not by * alone, see examples.
ex.:
# only match a single variable show_custom_vars = _VAR1
# show all host variables for hosts and all service variables for services show_custom_vars = *
# show all host variables for hosts and all host and service variables for services show_custom_vars = HOST* show_custom_vars = *
expose_custom_vars
Expose custom vars sets a list of custom variables
which is safe for all users/contacts to view.
They will be used in filtering and column selection
as well as in json result sets. Basically they will
be handled the same way as show_custom_vars except they
will not be displayed automatically.
Syntax is the same as show_custom_vars.
ex.:
expose_custom_vars = _VAR1
expand_user_macros
Expand user macros ($USERx$) for host / service commands and custom variables. Can be specified more than once to define multiple user macros to expand. Be warned, some user macros can contain passwords and expanding them could expose them to unauthorized users. Use * as wildcard, ex.: USER*
Defaults to 'ALL' which means all user macros are expanded, because its limited to admin users anyway.
ex.:
expand_user_macros = USER1 expand_user_macros = USER10-20 expand_user_macros = PLUGIN* expand_user_macros = ALL # expands all user macros expand_user_macros = NONE # do not expand user macros
show_error_reports
Show link to bug reports when internal errors occur. Set to '1' to show a error icon which links to a error report mail. Set to 'server' to log js error server side. Set to 'both' to log server side but still show the icon.
ex.: show_error_reports = both
skip_js_errors
don’t report some known harmless javascript errors
ex.: skip_js_errors = cluetip is not a function
strict_passive_mode
Normally passive checks would be marked as disabled. With this option set, disabled checks will only be displayed as disabled if their last result was active. Otherwise they would be marked as passive checks. This option also changes the passive icon only to be shown when the last check was passive, otherwise the disabled icon will be displayed.
ex.:
strict_passive_mode = 1
hide_passive_icon
Normally passive checks would be displayed with a passive icon if their last result is passive. With this option, passive icon will be hidden in status details.
ex.:
hide_passive_icon = 0
hide_top
new in release v3.00hide_top sets the default value for showing/hiding the totals header on status pages. It can be set to one of:
-
auto(default) hides header initially on small screens -
1always hide header initially -
0always show header initially
ex.:
hide_top = auto
sitepanel
The sitepanel is used to display multiple backends/sites at a glance. With than 10 or more sites, the list of backends will be combined into the 'compact' site panel which just displays the totals of available / down / disabled sites. The 'compact' panel will also automatically be used if you use sections. With more than 50 backends, the 'collapsed' panel will be selected in 'auto' mode. With more than 100 backends, the 'tree' panel will be selected in 'auto' mode. Set sitepanel to list/compact/collapsed/tree/auto/off to change the default behavior.
ex.:
sitepanel = auto
apache_status
You can integrate the output of apache status into Thruk. The following list of apache status pages will be accessible from the performance info page. Make sure the page is accessible from Thruk, credentials will be passed through. So both, basic authentication or ip based authentication would be possible. Read more about Apaches mod_status here: http://httpd.apache.org/docs/current/mod/mod_status.html
ex.:
<apache_status> Site http://127.0.0.1:5000/server-status System http://127.0.0.1/server-status Other http://127.0.0.1/server-status </apache_status>
Connection Settings
check_local_states
DEPRECATED: please use LMD when using multiple backends.
backend_debug
Set logging of backend in verbose mode. This only makes sense when debug logging is activated.
ex.:
backend_debug = 1
connection_pool_size
Use connection pool when accessing multiple sites. Increases the performance because backends will be queried parallel but uses around 10mb of memory per pool member. Disabled when set to 0, number of concurrent connections otherwise.
ex.:
connection_pool_size = 5
use_lmd_core
new in release v2.12Enable lmd connection handling. Set to 1 to enable. LMD handles all backend connections in a separate process which will be started automatically with thruk if enabled. Read more on lmd at: https://github.com/sni/lmd or here LMD.
ex.:
use_lmd_core = 0
lmd_core_bin
Path to lmd binary.
ex.:
lmd_core_bin = /usr/local/go/src/github.com/sni/lmd/lmd/lmd
lmd_core_config
Path to additional lmd configuration. The sites will be automatically generated. Can be used multiple times.
ex.:
lmd_core_config = /etc/thruk/lmd.ini lmd_core_config = /etc/thruk/lmd.ini.d/*.ini
lmd_options
Set some extra command line options when starting lmd.
ex.:
lmd_options = -debug-deadlock 30 -debug-profiler localhost:6060
lmd_timeout
Thruk waits this timeout for lmd to respond, otherwise it gets killed and restarted. Set to 0 to turn off automatic restarts (it will still be started if it is not running).
ex.:
lmd_timeout=5
lmd_remote
Instead of using LMD managed by Thruk, you can run your own LMD and let Thruk use that one instead
ex.:
lmd_remote=localhost:3333
logcache
Enables caching logfiles for faster access and less memory usage for the naemon process. Cache supports only Mysql. Preferred type is Mysql. Format is a Mysql connection string like 'mysql://hostname:port/db'. Using a cache dramatically decreases cpu and memory usage of Thruk and Naemon when accessing logfiles, for example when creating reports.
ex.:
logcache = mysql://user:password@localhost:3306/thruk_log_cache
logcache_import_exclude
new in release v2.10Define filter which prevents the logcache from overgrowing with useless log messages. Since the main reason for the logcache are availability reports it is ok to remove some entries. Can be used multiple times.
ex.:
logcache_import_exclude = "Warning: Passive check result was received for" logcache_import_exclude = "wproc: " logcache_import_exclude = "PASSIVE SERVICE CHECK: " logcache_import_exclude = "PASSIVE HOST CHECK: " logcache_import_exclude = "Warning: Check of " logcache_import_exclude = "Warning: External command parse error " logcache_import_exclude = "EXTERNAL COMMAND: PROCESS_SERVICE_CHECK_RESULT" logcache_import_exclude = "EXTERNAL COMMAND: PROCESS_HOST_CHECK_RESULT" logcache_import_exclude = "External command error: Failed validation"
logcache_delta_updates
new in release v2.12This option enables/disables the delta updates of the logcache whenever somebody opens a page which requires logfiles, ex.: the showlog page. This improves the responsiveness of the page but you miss the latest log entries since the last manual update.
ex.:
logcache_delta_updates = 1
logcache_worker
When having multiple sites, you can change the number of parallel updates with the logcache_worker option. Setting worker number to 1 disables parallel execution.
ex.:
logcache_worker = auto
logcache_clean_duration
Default duration when running thruk logcache clean. See the
time definitions page for available options.
ex.:
logcache_clean_duration = 2y
logcache_compact_duration
Default duration when running thruk logcache compact. Compact removes
duplicate alerts having the same state. It also removes basically everything
not required for sla reports and keeps a few extras like notifications.
ex.:
logcache_compact_duration = 10w
logcache_auto_bypass
Define wether logcache will be bypassed if the start / end time of a log queries is outside the range of the cache.
-
0: never, only use cached logs and return empty result if outside cached range. (default) -
1: partially, bypass logcache if start and end are outside cache range, otherwise return partially result. -
2: always, bypass logcache if either start or end are outside the cache range.
ex.:
logcache_auto_bypass = 0
logcache_import_command
The import command replaces the builtin logcache update with an external script which is then responsible for updating the logcache database. This might be useful if you pull the logfiles from a ndo/ido database and then manually import those files.
There are some useful environment variables set before the script is started:
-
standard macros as listed in CLI Environment
-
THRUK_BACKENDS is a semicolon separated list of the selected backends.
-
THRUK_LOGCACHE is the connection string to the thruk logcache database.
-
THRUK_LOGCACHE_MODE is either 'import' on first initial import or 'update' for further consecutive updates.
ex.:
logcache_import_command = .../importscript.sh
logcache_fetchlogs_command
The fetchlogs command is very similar to the logcache_import_command but it
replaces only the the fetching logs part from the builtin logcache.
This script should return the plain text logfiles on stdout (standard
naemon/nagios logfile format). This might be useful if you pull the logfiles
from a ndo/ido database.
|
mixedsetup
When having mixed backend cores, this command can be overridden in the peer configuration. |
See ./support/icinga2_ido_fetchlogs.sh for an example.
There are some useful environment variables set before the script is started to control which logs should be fetched:
-
REMOTE_USER contains the current user.
-
THRUK_BACKEND is a the id of the backends to import.
-
THRUK_LOGCACHE_START is start date to fetch
-
THRUK_LOGCACHE_END is the end date to fetch
-
THRUK_LOGCACHE_LIMIT is the optional limit of logfiles to fetch
ex.:
logcache_fetchlogs_command = IDO_DB_HOST=127.0.0.1 IDO_DB_PORT=3306 IDO_DB_USER=root IDO_DB_PW=root IDO_DB_NAME=icinga ./support/icinga2_ido_fetchlogs.sh mysql
logcache_pxc_strict_mode
If you are using a mysql database with galera replication such as MariaDB Cluster, Percona XtraDB Cluster or Galera Cluster it is a good idea to avoid locks and optimize/repair table statements since they are not properly replicated.
Especially in Percona XtraDB Cluster > 5.6 the default setting of pxc_strict_mode will disable locks all together.
This setting will make the logcache work in that case. More information about pxc_strict_mode available here: - Percona documentation
ex.:
logcache_pxc_strict_mode = 1
delay_pages_after_backend_reload
Delay the page delivery until the backends uptime is at least this amount of seconds. Displaying pages soon after backend restarts may display wrong results and all services are pending. Enable this if you experience problems with pending services after reloading your backend. Should be obsolete with Livestatus versions greater than 1.2 ex.: setting this to 10 would start serving pages 10 seconds after the backend reload
ex.:
delay_pages_after_backend_reload = 10
ssl_verify_hostnames
Can be set to enable / disable hostname verification for https connections. For
example for the cookie login, https backends or oauth requests. It is not recommended
to disabled hostname verification, set ssl_ca_path or ssl_ca_file instead.
ex.:
ssl_verify_hostnames = 1
ssl_ca_path
Sets path to your certificates. Either set ssl_ca_path or ssl_ca_file.
Not both. Defaults to ssl_ca_file = Mozilla::CA::SSL_ca_file() if Mozilla::CA perl
module is installed or ssl_ca_path = '/etc/ssl/certs' otherwise.
ex.:
ssl_ca_path = /etc/ssl/certs
ssl_ca_file
Sets path to your ca store. See ssl_ca_path for details.
ex.:
ssl_ca_file = /etc/ssl/certs/ca.pem
Cookie Authentication Settings
cookie_auth_login_url
Specifies the url where non-authenticated users will be redirected too.
ex.:
cookie_auth_login_url = thruk/cgi-bin/login.cgi
cookie_auth_restricted_url
Specifies the url against the cookie auth provider will verify its credentials.
ex.:
cookie_auth_restricted_url = http://localhost/thruk/cgi-bin/restricted.cgi
cookie_auth_session_timeout
Specifies the timeout for idle sessions. Session will be removed if not used within this timeperiod.
ex.:
cookie_auth_session_timeout = 86400
cookie_auth_session_cache_timeout
Specifies the amount of seconds in which subsequent requests won’t verify authentication again. Set to zero to disable storing encrypted credentials in the filesystem and disabling revalidation of active sessions (sessions will never invalidate).
ex.:
cookie_auth_session_cache_timeout = 30
cookie_auth_session_cache_fail_timeout
Just like successful logins are cached for a few
seconds (cookie_auth_session_cache_timeout), failed logins are cached as well
to prevent denial of service attacks with invalid credentials. cookie_auth_session_cache_fail_timeout sets the amount
of seconds to cache failed logins. Set this to zero disabled invalidation of the
cache.
ex.:
cookie_auth_session_cache_fail_timeout = 30
cookie_auth_login_timeout
Timeout for internal sub request on authentication url. Defaults to 10 seconds and can be disabled by setting it to zero.
ex.:
cookie_auth_login_timeout = 10
cookie_auth_domain
Cookie domain is usually set automatically. Use this option to override the default value. Domains have to contain at least two periods. Useful for single sign on environments.
ex.:
cookie_auth_domain = .domain.com
cookie_auth_login_hook
Hook script which is called on every successful login. The REMOTE_USER
environment variable will be set to the username of the current logged
in user. Useful to do magic stuff on each login. The REMOTE_USER_GROUPS
environment variable contains semicolon separated list of contactgroups.
THRUK_REQ_URL contains the current url.
Available standard environment variables are listed on the
CLI Environment page.
ex.:
cookie_auth_login_hook = ./bin/hook.sh
|
background job
The login page will wait for the hook to finish, so if some sync jobs should be started in the background the hook itself needs to take care of this. If it’s a shell script, you could add something this this to the head of the script: |
cookie_auth_disable_after_failed_logins
new in release v2.12Disable account after this number of failed login attempts. This feature will be disabled if set to zero.
Default: 10
ex.:
cookie_auth_disable_after_failed_logins = 3
locked_message
new in release v2.46The error message when an account is locked, may contain html.
ex.:
locked_message = account is locked, please contact an administrator
cookie_auth_verbose
new in release v2.32Increase logging of cookie authentication related things. This usually gets printed to the apache error log.
Default: 0
ex.:
cookie_auth_verbose = 3
OAuth2 Authentication Settings
See some example configurations here: OAuth2 Examples.
When the oauth provider needs to configure an allowed callback url, set the url of the login page, ex.:
or without <omdsite> when not using OMD.
auth_oauth
Set oauth (oauth2) authentication provider
ex.:
<auth_oauth>
<provider name>
login = "Login with OAuth" # Value of the login button.
icon = "uil uil-enter" # CSS class for button icon.
client_id = <required> # Client_id as set from the oauth provider.
client_secret = <required> # Secret key from the oauth provider
scopes = openid profile email # Scopes required to access user information
auth_url = https://oauthserver/oauth2/v1/authorize # Initial authenticator redirect url
token_url = https://oauthserver/oauth2/v1/token # URL to exchange code into token
api_url = https://oauthserver/oauth2/v1/userinfo # API endpoint to retrieve user information from
login_field = login # Hash key from user info to get the actual username from. If not set, Thruk will try 'login', then 'email'
groups_field = groups # Hash key from user info to fetch teams from. If not set, Thruk will try 'groups'
#enable_pkce = 0 # enable oauth 2.1 pkce workflow if set to 1. Disabled by default
#https_proxy = http://<server>:<port> # optional proxy to use for accessing URLs from above
#ssl_verify_hostnames = 1 # skip ssl hostname verification when set to 0
#autologin = 0 # automatically select and submit this provider when set to 1
</provider>
</auth_oauth>
Command Settings
cmd_defaults
Set the default checked state for command options.
ex.:
<cmd_defaults> ahas = 0 # For Hosts Too broadcast_notification = 0 # Broadcast force_check = 0 # Forced Check force_notification = 0 # Forced Notification send_notification = 1 # Send Notification sticky_ack = 1 # Sticky Acknowledgement comment = "" # Default comment persistent_comments = 1 # Persistent Comments persistent_ack = 0 # Persistent Acknowledgement Comments ptc = 0 # For Child Hosts Too use_expire = 0 # Use expire time ( for cores which support it) childoptions = 0 # 0 = Do nothing with child hosts, 1 = Triggered downtime for all child hosts, 2 = Non-triggered downtime for all childs hostserviceoptions = 0 # 0 = Do nothing with services, 1 = Schedule downtime for all services </cmd_defaults>
force_sticky_ack
Forces acknowledgments to be sticky.
ex.:
force_sticky_ack = 1
force_send_notification
Forces sending a notification for acknowledgments.
ex.:
force_send_notification = 1
force_persistent_ack
Forces comments on acknowledgments to be persistent.
ex.:
force_persistent_ack = 1
force_persistent_comments
Forces normal comments to be persistent.
ex.:
force_persistent_comments = 1
downtime_duration
Default duration of new downtimes in seconds. Default is 2 hours.
ex.:
downtime_duration = 7200
downtime_max_duration
Maximum duration of new downtimes. Use quantifiers like d=days, w=weeks, y=years to set human readable values. Default is unlimited.
ex.:
downtime_max_duration = 4w
has_expire_acks
new in release v3.00Show expire acknowledgement form.
ex.:
has_expire_acks = 1
expire_ack_duration
Default duration of acknowledgements with expire date. Default is one day.
ex.:
expire_ack_duration = 86400
reschedule_spread
Default spread of rescheduled checks in seconds. Default is none. Options are 0, 10, 30, 60, 300, 900, 1800, 3600.
ex.:
reschedule_spread = 0
cmd_quick_status
Configure which commands should be available as quick status commands.
ex.:
<cmd_quick_status> reschedule = 0 # Reschedule next check downtime = 0 # Add/remove downtimes comment = 0 # Add/remove comments acknowledgement = 0 # Add/remove acknowledgements active_checks = 0 # Enable/disable active checks notifications = 0 # Enable/disable notifications eventhandler = 1 # Enable/disable eventhandler submit_result = 0 # Submit passive check result reset_attributes = 0 # Reset modified attributes </cmd_quick_status>
command_reschedule_alias
When you want to reschedule passive checks for which the result is fetched by an agent (For example check_mk or some scenarios of check_multi). You usually want to reschedule the agent instead of the passive check.
The command reschedule alias can be used to translate the reschedule command from the passive service to the active agent service.
command_reschedule_alias = pattern;master_service_description
-
The pattern will be tested against the service description and the command_name of the passive check.
-
The resulting service name be on the same host and the contact must be authorized for that service too.
-
The pattern must be a valid perl regular expression.
-
Duplicates will be removed. So if you reschedule 10 services which result in the same master service will only trigger one reschedule.
-
Only passive services will be translated
In this example, all passive check_mk checks will trigger the active agent check and therefore allow you to reschedule passive checks directly from the problems page.
ex.:
command_reschedule_alias = ^check_mk\-(?!inventory);Check_MK
use_feature_recurring_downtime
Use recurring downtime, shows recurring downtime links.
ex.:
use_feature_recurring_downtime = 1
use_service_description
Use service’s description instead of display name.
DEPRECATED use service_description_source instead.
ex.:
use_service_description = 1
host_name_source
new in release v3.06Set alternative source of host name display. Listed attributes will be tried in given order and first non-empty value wins. Custom variables are possible ex.: _NAME, name will first try the _NAME custom variable and use the host.name as fallback. Useful attributes are ex.: name, alias, address, display_name or custom variables
Note: hosts will always be ordered by host_name
ex.:
host_name_source = display_name, name
service_description_source
new in release v3.06Set alternative source of service description display. Listed attributes will be tried in given order and first non-empty value wins. Custom variables are possible ex.: _NAME, description will first try the _NAME custom variable and use the service.description as fallback. Useful attributes are ex.: description, display_name or custom variables
Note: services will always be ordered by description.
ex.:
service_description_source = display_name, description
use_feature_trends
Use trends, shows trend links.
ex.:
use_feature_trends = 1
use_wait_feature
Waiting is a livestatus feature. When enabled, Thruk will wait after rescheduling hosts/services checks until the check has been really executed up to a maximum of 10 seconds. Adjust the time waiting with the 'wait_timeout' option.
ex.:
use_wait_feature = 1
wait_timeout
Amount of seconds to wait until a rescheduled check finishes. Thruk will wait this amount and display the result immediately.
ex.:
wait_timeout = 10
require_comments_for_disable_cmds
If set to 1, the user has to enter a comment for all disable active checks / disable notifications / disable event handler commands. These comments are automatically prefixed with the command name and will be deleted when checks / notifications / handlers are enabled again. They are also used by the 'reenable_actions' utility.
ex.:
require_comments_for_disable_cmds = 1
Cron Settings
cron_file
Specify a file which is then completely under the control of Thruk. It will be used to store cronjobs, ex. for reports. The file has to be writable by Thruk.
ex.:
cron_file = /tmp/thruk_cron.tmp
cron_pre_edit_cmd
The pre edit cmd can be used to do run a command just before Thruk will edit the crontab.
ex.:
cron_pre_edit_cmd = /usr/bin/crontab -l > /tmp/thruk_cron.tmp
cron_post_edit_cmd
The post edit cmd is necessary for OMD where you need to reload the crontab after editing or for replacing the users cron with the edited file.
ex.:
cron_post_edit_cmd = crontab /tmp/thruk_cron.tmp
thruk_bin
Path to your thruk executable. Will be used in cronjobs.
ex.:
thruk_bin = /usr/bin/thruk
Action Menu Settings
The Action Menu is a way to create custom icons and menus for every host or service. There are two ways to set the menu. First one is to directly assign the menu json data into the _THRUK_ACTION_MENU custom variable of your host or service. Or you can just put a placeholder into the _THRUK_ACTION_MENU custom variable and define the actual menu in 'action_menu_items'. You may add multiple action icons or even multiple menus for each host or service.
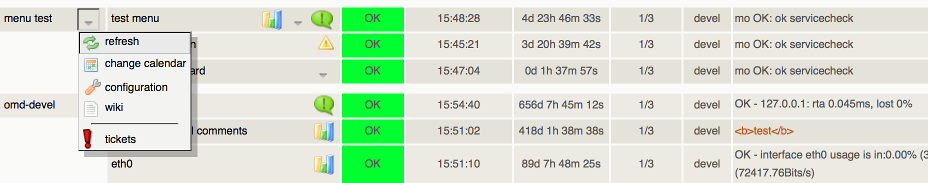
See the Action Menu section from the advanced topics for more examples and details.
action_menu_items
new in release v1.86Defines the menu used by placeholders from the '_THRUK_ACTION_MENU' custom variable. The menu is a key/value pair with the name and the menu description in json format. The menu can either be a single icon/menu or a list of menus and icons.
A simple menu could look like this, note that the menu has to be in a single line without newlines and all newlines from the example have to be removed in order to try that. But its more readable this way. You can also use a trailing backslash to write the menus on multiple lines.
Sample menu with two items and a separator:
{
"icon":"../themes/{{theme}}/images/dropdown.png",
"title": "sample menu",
"menu": [
{
"icon": "uil-redo",
"label": "refresh",
"action": "server://refresh/$HOSTNAME$"
},
{
"icon": "fa-rocket",
"label": "example",
"action": "server://example/$HOSTNAME$/$SERVICEDESC$"
},
"-",
{
"icon": "../themes/{{theme}}/images/page_white_text.png",
"label": "wiki",
"action": "http://company-wiki/pages/$HOSTNAME$"
}
]
}
A menu has the following attributes:
-
iconicon for the menu itself. You can use{{theme}}as placeholder in the url and{{remote_user}}for the user name. Within OMD, the the site variable{{site}}must be prepended. An Icon can be either:-
a path to an image
-
an unicon icon when starting with
uil-(list of unicon icons) -
a font-awesome icon when starting with
fa-(list of font awesome icons)
-
-
titletitle of the menu, will be display on mouse over. -
hiddenmenu will be hidden if true. -
menuthe actual menu definition as a list '[…]' of sub items. -
…arbitrary attributes will be used as attributes of the menu icon html element.
A single "-" item can be used as a menu item separator.
The menu item can have the following attributes:
-
iconicon for the menu item. You can use{{theme}}as placeholder in the url. Within OMD, the the site variable{{site}}must be prepended. An Icon can be either:-
a path to an image
-
an unicon icon when starting with
uil-(list of unicon icons) -
a font-awesome icon when starting with
fa-(list of font awesome icons)
-
-
labellabel name of the menu item. -
menulist of sub menu items. -
actionurl or action which will be run or opened. This can either be a http(s) link or a serveraction in the form server://actionname/argument1/argument2/… the actionname must be a reference to a command from 'action_menu_actions'. You may use{{macros}}here too. Also javascript: links are valid, for examplejavascript:alert('$HOSTNAME$'). -
targetUse '_blank' here to open link in a new window. -
onclickconfirmation dialog or any other callback, ex: "return(confirm('Really restart service?'));" -
close_timeouttimeout till the result popup will close, defaults to 5 seconds if ok or 30 seconds if failed. Set to zero to never close the result popup. -
disabledmenu item will be disabled. -
hiddenmenu item will be hidden if true. -
htmlraw html code instead of any other logic. -
…arbitrary attributes will be used as attributes of the menu item link html element.
action menu macros
The following macros can be used in the icon, action, title and label attribute.
-
{{theme}}contains the current selected user theme -
{{remote_user}}contains the user name itself. (Do not rely on this value, a user can change the url by himself) -
{{prefix}}the url path prefix, ex.: /thruk -
{{site}}the OMD site name. -
$HOSTNAME$contains the host name. -
$SERVICEDESC$contains the service description.
action menu variables
The following variables can be used in the action attribute when specifying a server action or a http(s) url.
-
$HOSTNAME$contains the host name -
$HOSTADDRESS$contains the host address -
…
and many more. You’ll find a complete list of macros on the macros page.
Sample icons with two action icons:
[
{
"icon":"../themes/{{theme}}/images/criticity_1.png",
"action":"http://splunk/abc/hostid=$_HOSTHOSTID$",
"target":"_blank"
},
{
"icon":"uil-redo",
"action":"server://refresh/$HOSTNAME$",
}
]
Variant 1 - put your action menus into a separate folder.
*thruk_local.conf:*
action_menu_items_folder /etc/thruk/action_menus/
Menu files must have the .json file extension and contain the raw json
definition of the action menu. One menu per file. The menu can be referenced
by the filename later. For example if you filename is /etc/thruk/action_menus/some_menu.json then
you can access the menu by the name some_menu.
Variant 2 - reference a menu from an external file:
*thruk_local.conf:*
<action_menu_items>
standard_menu = file:///etc/thruk/standard_menu.json
</action_menu_items>
Menu files must contain the raw json definition of the action menu.
Variant 3 - reference to a pre defined menu:
*thruk_local.conf:*
<action_menu_items>
standard_menu = {"icon":"/thruk/themes/{{theme}}/images/dropdown.png",\
"title": "test title",\
"menu":[\
{"icon":"uil-redo",\
"label":"refresh",\
"action":"server://refresh/$HOSTNAME$"}\
]\
}
</action_menu_items>
*host.cfg:*
define host {
host_name localhost
...
_THRUK_ACTION_MENU standard_menu
}
Variant 4 - define the menu in object config only:
This obviously adds some overhead to your objects, so better use the other variants unless you want to change the menu from external commands.
*host.cfg:*
define host {
host_name localhost
...
_THRUK_ACTION_MENU {"icon":"/thruk/themes/{{theme}}/images/dropdown.png", "title": "test title", "menu":[ {"icon":"uil-redo","label":"refresh","action":"server://refresh/$HOSTNAME$"}]}
}
action_menu_items_folder
new in release v2.10Organize action_menu_items in a folder. Each file in this folder will be read as action menu.
This folder may also contain .js files since version 2.24.
Both examples are equivalent and result in the same menu assuming there is
a /etc/thruk/action_menus/host_menu.json file.
action_menu_items_folder = /etc/thruk/action_menus/
<action_menu_items>
host_menu = file:///etc/thruk/action_menus/host_menu.json
</action_menu_items>
action_menu_apply
new in release v1.86With apply rules adding action menus is made easy and independent from the actual
object configuration. You can setup a few regular expression rules which then add
the corresponding action menu to matching hosts and services. The syntax is
menu_name = Hostpattern;Servicepattern
ex.:
<action_menu_apply> host_menu = .*;$ # matches all hosts only service_menu = .*;.+$ # matches all services on all hosts special_menu = ^Host;Service$ # matches an exact service on one host only cpu_menu = .*;CPU # matches all services starting with 'CPU' host_menu = ^Host # matches all hosts starting with 'Host' (incl. services) demo_menu = ^Demo;.*$ # matches all services on the 'Demo' host demo_menu = ^Test; # a menu name can be used multiple times </action_menu_apply>
action_menu_actions
new in release v1.86Defines the available server commands from action_menu_items. Key/Value pair of the name of the script and the corresponding command. The command has to be a full path program and not just a shell command. Therefore you do not have to use quotes because the arguments are not interpreted by a shell before execution due to security reasons.
It is possible to use most standard Macros and the username is available in the REMOTE_USER
environment variable.
ex.:
<action_menu_actions>
example = /usr/local/bin/sample.sh $HOSTNAME$ $SERVICEDESC$ $USER20$
refresh = /usr/local/bin/refresh.sh otherargs
</action_menu_actions>
Icinga Settings
enable_icinga_features
This one activates all icinga specific features. If not set, Thruk will try to auto-detect your backends. Currently auto detection will only work within OMD. Don’t enable it unless all your backends are icinga.
ex.:
enable_icinga_features = 1
Shinken Settings
enable_shinken_features
This one activates all problem/impact and criticity features. Currently it will only work with shinken backends. Don’t enable it unless all your backends are shinken. If not set, it will be automatically enabled when using only shinken backends.
ex.:
enable_shinken_features = 1
priorities
Set the names of the priority (criticity in shinken). Currently this will only work with shinken backends.
ex.:
<priorities> 5 = Business Critical 4 = Top Production 3 = Production 2 = Standard 1 = Testing 0 = Development </priorities>
Other Settings
no_external_job_forks
Normally reports will be generated in an external process to avoid timeouts on long running reports. Use this switch to turn external jobs off and generate reports directly. Make sure they are finished within 40seconds which is the default fcgi timeout.
ex.:
no_external_job_forks = 1
thruk_init
Path to your thruk init script. Will be used to restart thruk.
ex.:
thruk_init = /etc/init.d/thruk
cookie_path
Path used for cookies. Do not change unless you have weird url rewrites which breaks setting cookies.
ex.:
cookie_path = /
cookie_secure_only
Sets all cookies with secure=1 if enabled.
ex.:
cookie_secure_only = 1
Component Thruk::Backend
Enter your backend connection settings here. See Backend Configuration for details.
peer
-
namename for this connection -
typetype of this connection. Can be 'livestatus' or 'http'. -
hiddenshould this peer be hidden initially ( can be reenabled via gui switch ) Only useful with more than one backend. Setting this option removes this backend from any report or cli action unless backends are specified explicitly. -
displaySet to 0 if you want to hide this backend from the default view. This can be changed by the site panel again. In opposite to the 'hidden' flag, backends set to display=0 are still used for automatic actions and reports. -
groupsif set, only contacts from these groups have access. You may add multiple groups separated by comma. Users without the right contactgroup don’t even see that there is a backend. Note that this implies one extra backend request per page. (DEPRECATED - please do not use) -
authoritativeWhen having multiple backends, set this to true to gather authorization information only from this backend(s). -
activeBackend will be skipped as if it’s not configured at all if set to 0. -
sectionto group backends/sites by different sections, enter a section. -
state_hostDEPRECATED - please use LMD when using multiple backends. -
logcacheSet logcache connection for this specific backend. Set to0to disable logcache for this site. -
logcache_fetchlogs_commandOverride global logcache_fetchlogs_command. -
options-
peeraddress of this connection. (can be used multiple times when using LMD) -
resource_fileresource_file for this peer (used for macro replacement) -
authsecret key for http connections. -
remote_nameremote site name for http connections (required if remote instance is connected to multiple backends) -
fallback_peerfallback connection address. (optional, can be used multiple times, used when all peer addresses fail, only works with LMD) -
certoptional client certificate for tls connections -
keyoptional client key for tls connections -
ca_fileca file to verify tls server -
verifyset to 0 to disable any tls verification -
verifycn_nameset to expected remote server hostname (used in certificate verification) -
proxyoptional proxy for http backends (ex.: http://proxyhost:port) -
host_namessh host name (currently only used from the node-control module) -
site_namessh user name (currently only used from the node-control module)
-
-
configtool-
core_typeGive the config parser a hint about your config. Can be 'naemon', 'nagios', 'icinga' or 'shinken'. -
core_confPath to your naemon.cfg / nagios.cfg / icinga.cfg. Read all object directories and files from this config file. -
obj_check_cmdCommandline to verify the config. Use something like 'sudo -u root /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg' if you have different user for Thruk and the monitoring core. See http://monitoring-portal.org/wbb/index.php?page=Thread&postID=224902#post224902 for an example. -
obj_reload_cmdCommandline to reload the config. -
obj_readonlyFilename pattern to define readonly objects. For example for generated config files. The same effect can be achieved by adding "# thruk: readonly" on top of a object config file. -
obj_dirPath to your objects. Enables the objects editor. Reads all *.cfg from this folder and all subfolder. (only needed when not using 'core_conf') -
obj_filePath to a single objects file. Enables the objects editor. Both 'obj_dir' and 'obj_file' can be specified more than once. (only needed when not using 'core_conf') -
obj_excludeSpecify some exception pattern for the obj_dir. (only needed when not using 'core_conf') -
git_base_dirOverride global 'git_base_dir' value. -
disableSet to1to disable config tool for this backend (ex.: when detected automatically for http backends)
-
-
lmd_options-
flagsflags to passthrough to lmd -
…any attribute will be just passed into the connection section of the lmd.ini, see example below.
-
ex.:
<Component Thruk::Backend>
<peer>
name = Local Naemon
type = livestatus
hidden = 1 # makes this backend hidden by default
groups = admins,locals # makes this backend only visible to the
# admin and the locals contactgroup
<options>
peer = /tmp/livestatus.socket
</options>
<configtool>
core_conf = /etc/naemon/naemon.cfg
obj_check_cmd = /etc/init.d/naemon checkconfig
obj_reload_cmd = /etc/init.d/naemon reload
</configtool>
</peer>
<peer>
name = External Icinga
type = livestatus
<options>
peer = 172.16.0.2:9999
</options>
<lmd_options>
flags = ['Icinga2']
</lmd_options>
</peer>
<peer>
name = External Shinken
type = livestatus
<options>
peer = 172.16.0.3:50000
fallback_peer = 172.16.0.4:50000 # will be used as fallback
</options>
</peer>
<peer>
name = Another Thruk
type = http
<options>
peer = http://172.16.0.4/thruk/
auth = secret_key_from_remote_instance
remote_name = id1 # required if remote site has multiple backends connected itself
</options>
</peer>
<peer>
name = TLS Livestatus
type = livestatus
<options>
peer = tls://172.16.0.2:9999
cert = client.pem
key = client.key
ca_file = server.crt
verify = 1
</options>
</peer>
</Component>
Component Thruk::Plugin::ConfigTool
Enable config tool by setting path to different components config files. Users with the roles 'authorized_for_configuration_information' and 'authorized_for_system_commands' will then have access to the config tool. You don’t have to restart Thruk when changing the config with the config tool.
ex.:
<Component Thruk::Plugin::ConfigTool> show_plugin_syntax_helper = 1 thruk = .../thruk_local.conf cgi.cfg = .../cgi.cfg htpasswd = .../htpasswd pre_obj_save_cmd = .../hook.sh post_obj_save_cmd = .../hook.sh git_base_dir = /etc/naemon/conf.d/custom/ show_summary_prompt = 1 #edit_files = some/extra/files/to.edit # deprecated extra_custom_var_host = _WORKER extra_custom_var_service = _SNMP_COMMUNITY, _OTHER_CUSTOM_VARIABLE obj_readonly = readonly files regular expression # default_keys_host = host_name use:generic-host alias address contact_groups:example # default_keys_service = service_description use host_name check_command contact_groups # default_keys_contact = contact_name use alias email can_submit_commands # default_keys_... = ... # set default keys for any type </Component>
show_plugin_syntax_helper
Enable/Disable the plugin syntax helper. When enabled, Thruk will run the plugins with "plugin -h" to get the help information.
thruk
Path to your thruk_local.conf. Enables adjusting Thruks config if set.
cgi.cfg
Path to your cgi.cfg. Enables adjusting the cgi.cfg if set.
htpasswd
Path to your htpasswd. Enables user management based an Apaches basic auth with htpasswd.
pre_obj_save_cmd
Run a command before saving object config files. Save will be canceled if the command returns non-zero exit code. Command will be run with 'pre' as first argument and the root config folder as second argument.
The following environment variables will be set:
-
standard macrosas listed in CLI Environment -
THRUK_BACKEND_IDinternal id of the current edited backend -
THRUK_BACKEND_NAMEname of the current edited backend -
THRUK_SUMMARY_MESSAGEuser supplied change summary title -
THRUK_SUMMARY_DETAILSuser supplied change details
post_obj_save_cmd
Run a command after saving object config files. Command will be run with 'post' as first argument and the root config folder as second argument.
An example can be found in 'examples/config_tool_git_checkin'.
The following environment variables will be set:
-
standard macrosas listed in CLI Environment -
THRUK_BACKEND_IDinternal id of the current edited backend -
THRUK_BACKEND_NAMEname of the current edited backend -
THRUK_SUMMARY_MESSAGEuser supplied change summary title -
THRUK_SUMMARY_DETAILSuser supplied change details
git_base_dir
If not all config folders are managed by git, then you can specify a directory which is used to display the history. Should point to a directory which is part of a git repository. This config setting is only used for the history support in the configuration tool. The 'git_base_dir' may be overridden by an per backend value.
show_summary_prompt
Thruk will show a prompt to input a change summary if a 'post_obj_save_cmd' is set. You can use this option to suppress that prompt.
edit_files
DEPRECATED: please use the editor plugin now.
Specify some extra files which can then be edited by the Thruk configtool text editor. Can be used multiple times. When used with a directory, all files below can be edited.
extra_custom_var_host
Extra custom variable attribute for hosts which will be available in the dropdown list when editing a host. Can be used multiple time and accepts comma separated lists.
extra_custom_var_service
Extra custom variable attribute for services which will be available in the dropdown list when editing a service. Can be used multiple time and accepts comma separated lists.
obj_readonly
Use obj_readonly regular expressions which will be appended to the backend
specific readonly patterns from the Component Backend peer configtool. The same
effect can be achieved by adding "# thruk: readonly" on top of a object config file.
Read details on the configtool section.
default_keys_host
Space separated list of default attributes when creating a new host. Can contain custom variables
like _VAR. Append default value separated by a :. This obviously means you
cannot use spaces or colons in attributes or default values.
ex.:
default_keys_host = host_name use:generic-host alias address contact_groups _WORKER:local
default_keys_service
see default_keys_host.
default_keys_contact
see default_keys_host.
Component Thruk::Plugin::Panorama
The 'Panorama' plugin is a nice, fully customizable dashboard allowing you to build your own panorama views.
ex.:
<Component Thruk::Plugin::Panorama> default_dashboard = 1,3,7,4 readonly = 0 full_reload_interval = 10800 geo_map_default_center = 13.74,47.77 geo_map_default_zoom = 5 extra_fonts = CompanyFont1, CompanyFont2 new_files_start_at = 1 default_state_order = down, unreachable, ... default_maintenance_text = "this dashboard is currently in <b>maintenance mode</b>" </Component>
default_dashboard
Contains a comma separated list of dashboards you want to show by default.
readonly
Make panorama dashboard readonly. The user cannot add, remove or change panels and tabs. Commands may still be send according to the user permissions.
dashboard_ignore_changes
Make panorama dashboard ignore changes. The user is allowed to change some parts of the layout, but nothing is saved. Commands may still be send according to the user permissions.
full_reload_interval
Full page reload every 3 hours to prevent memory leaks. Disabled when set to 0.
new_files_start_at
Normally new files start at index 1 but this can be changed here. This helps in situations when more than one Thruk installation has to create dashboards in the same folder.
default_state_order
Defines the order to determine the worst state for filter and group icons. Use
this to override the global default_state_order.
default_maintenance_text
Sets the default text when setting dashboards into maintenance mode. You can use html to format the text.
geo_map_default_center
Default coordinates (lon,lat) for new geo maps.
geo_map_default_zoom
Default zoom level for new geo maps.
wms_provider
WMS provider serve map tile data for geo maps according to http://dev.openlayers.org/docs/files/OpenLayers/Layer/WMS-js.html#OpenLayers.Layer.WMS.OpenLayers.Layer.WMS Find more wms provider here: http://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/WMS#OSM_WMS_Servers
<Component Thruk::Plugin::Panorama>
...
wms_provider = <providername> = ["<wms-url>", {"layers": "<layername>"}", {"properties": "..."}]
</Component>
Properties can be set according to: http://dev.openlayers.org/docs/files/OpenLayers/Layer-js.html
Some common properties are: attribution or numZoomLevels.
extra_fonts
Comma separated list of additional fonts which will be listed in the text label drop down selection.
Component Thruk::Plugin::Reports2
The 'Reports2' plugin creates sla reports in html or pdf format. You probably have to install puppeteer in a recent version.
ex.:
<Component Thruk::Plugin::Reports2> report_nice_level = 5 max_concurrent_reports = 2 report_base_url = http://host.local/thruk/cgi-bin/ pnp_export = script/pnp_export.sh grafana_export = script/grafana_export.sh report_from_email = User Name <example@mail.com> default_template = host_sla.tt </Component>
report_nice_level
Execute regular scheduled reports with this nice level.
max_concurrent_reports
new in release v1.88Maximum number of reports running at a time. If more reports are started, then they will be queued up. Default is 2.
report_base_url
Url used to replace relative links in html reports.
phantomjs
phantomjs is deprecated and no longer use. It has been replaced
with puppeteer. See the FAQ
for further information.
pnp_export
pnp_export defines a script which exports a PNP4nagios graph into a local file which then can be included in reports. PNP4nagios images are either exported locally by executing php or remotely fetched with wget. This works automatically in OMD, but only for local sites of course. To make this work without OMD, set the variable 'PNP_ETC' and 'PNP_INDEX' in the ~/.thruk file of your webserver. The PNP4nagios url is taken from the action url or from the notes url.
ex.:
export PNP_ETC="/etc/pnp4nagios" export PNP_INDEX="/usr/share/pnp4nagios/htdocs/index.php"
Remote PNP4nagios graphs will be fetched by wget and usually the graphs are password protected, so you may want to set a different wget command to specify a username and password. This can to be set by the 'PNP_WGET' variable in the ~/.thruk file of the webserver user. You may force to use wget by setting 'PNP_URL_PREFIX'.
ex.:
export PNP_WGET="wget -q --user=admin --password=secret" export PNP_URL_PREFIX="http://demo.thruk.org"
grafana_export
Override default script for exporting grafana graphs to png with grafana_export.
report_from_email
Set the from address used in e-mail reports. Format is "User Name <example@mail.com>"
default_template
Set the default template used for new reports.
statusmap_default_type
You may change the default map type of the statusmap here. Valid types are: 'table' and 'circle'
statusmap_default_groupby
And the statusmap default group by which has to be one of: 'parent', 'address', 'domain', 'hostgroup', 'servicegroup'
Component Thruk::Plugin::Minemap
The Minemap plugin gives an overview of your hosts and services.
ex.:
<Component Thruk::Plugin::Minemap> minemap_default_link = /thruk/cgi-bin/minemap.cgi </Component>
minemap_default_link
You may change the default minemap link here.
Component Thruk::Plugin::BP
The Business Process plugin gives the possibility to create and model your business processes. In order to edit and create new business processes you will need the roles:
-
authorized_for_configuration_information
-
authorized_for_system_commands
Configuration Example:
<Component Thruk::Plugin::BP> #spool_dir = /var/naemon/rw/check_results result_backend = naemon objects_save_file = /etc/naemon/conf.d/bp_generated.cfg objects_templates_file = /etc/naemon/conf.d/thruk_bp_templates.cfg objects_reload_cmd = /etc/init.d/naemon reload #pre_save_cmd = #post_save_cmd = #post_refresh_cmd = refresh_interval = 1 #favorite_custom_function = echo ; echo_function #worker = 5 #offline_grace_time = 180 #default_filter = add_recursive_output_filter #default_state_order = down, unreachable, ... #sync_downtime_ack_state = 0 read_only = 0 default_tab = local | remote | all </Component>
spool_dir
Results will be send back by using the spool folder. This folder should point to the 'check_result_path' of your core.
result_backend
As alternative to the spool_dir, a livestatus connection can be used to send results to the core. Set the name or key of the backend with this option.
config_backend
Use this backend to store the actual objects. Must be a backend of type http.
objects_save_file
Save objects to this file. Content will be overwritten.
objects_save_format
File format of the saved objects. Valid formats are 'nagios' and 'icinga2'.
objects_templates_file
User maintained file containing templates used for business process services.
objects_reload_cmd
Command to apply changes to the objects_save_file.
pre_save_cmd
Run this hook command before saving a business process. Along with the default environment variables set, there are two extra variables set which can be used:
-
THRUK_BP_FILE: contains the file name of the business process being saved
-
THRUK_BP_STAGE: is set to 'pre'
post_save_cmd
Run this hook command after saving a business process. The same environment variables will be used as in the pre_save_cmd, except stage is set to 'post'.
post_refresh_cmd
Run this hook command after refreshing business processes is completed. Ex.:
after every cron run of thruk bp all.
refresh_interval
Refresh interval defines how often business processes will be recalculated and refreshed. (in minutes).
Automatic bp calculations will be disabled if set to zero.
favorite_custom_function
Favorite custom function will be displayed on the 'Type' tab so you don’t have to select custom first. Syntax is <name>;<function>
worker
Set the number of parallel business process calculations. Setting it to 1 disables parallelization. Setting it to 0 tries to autodetect a suitable value.
Automatic bp calculations will be disabled if set to zero.
offline_grace_time
Set the time (in seconds) how long a business process will wait for offline backends to recover. During this time the business process will keep its last known state.
Default is 180 seconds.
offline_handling
Decide how to handle offline backends in business processes. Valid values are:
-
0- do nothing if backends are offline, simply skips calculation for affected BP -
1- continue calculation after grace period (default) -
2- set to unknown state if any backend is offline
default_filter
Add global filter to all business processes, can be set multiple times.
default_state_order
Defines the order to determine the worst state for worst/best aggregations. Use
this to override the global default_state_order.
sync_downtime_ack_state
Set downtime/acknowledgement for business process if all child nodes are in downtime/acknowledged. Valid values are:
-
0- disabled -
1- display only (default) -
2- set downtime/acknowledgement by external command
(does not work in combination with spool_dir)
read_only
Make all bp related pages readonly.
default_tab
Choose which tab should be displayed by default. Only useful if several http backends are in use.
Valid values are:
-
local- Local BPs (default) -
remote- Show remote BPs -
all- Show all BPs
User & Group Specific Overrides
Both, the 'Users' and the 'Groups' directive override default settings for single users or groups. In theory it’s possible to override each and every config setting from the thruk.conf but you will get funny results if you override fundamental settings like backends, paths and such things.
'Groups' are contact groups from your monitoring core and 'Users' are the contact names as they show up in the Thruk interface.
Groups
The groups directive overrides specific config settings for one group only. Group overrides are applied in alphabetical order. For example, if you have a user in group 'Admins' and in 'SuperAdmins', he will get all overrides from both groups, but the 'Admins' overrides will be superseded by the 'SuperAdmins'.
ex.:
# disable all commands, except reschedule for all users
command_disabled = 0-6,8-95,97-999
<Group admins>
# enable commands for admins again
command_disabled =
</Group>
Users
The users directive overrides specific config settings for one user only.
ex.:
<User guest>
# override single configuration item
show_error_reports = 0
can_submit_commands = 0
# also available for nested components
<Component Thruk::Plugin::Panorama>
default_dashboard = 1,3,7,4
</Component>
</User>
